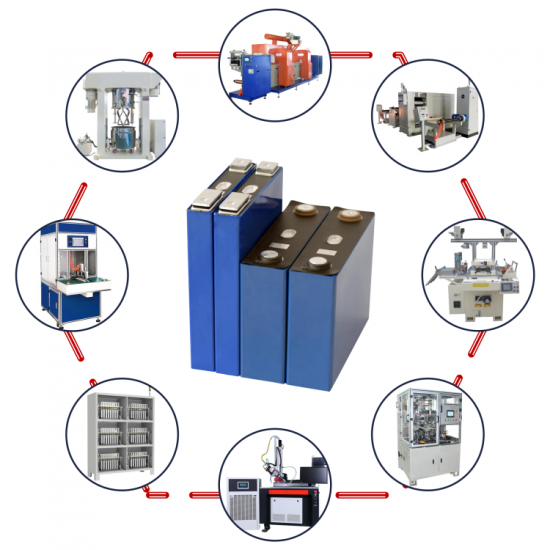
Prismatic battery assembly equipment refers to the machinery and tools used in the manufacturing process of prismatic lithium-ion batteries. Prismatic batteries are a specific type of lithium-ion battery that has a rectangular or prismatic shape, as opposed to cylindrical or pouch designs. These batteries are commonly used in various applications, including electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. Here are some key components and steps involved in prismatic battery assembly:
Electrode Coating Machine: This machine is used to precisely apply the positive and negative electrode materials onto metal foils. It ensures an even and consistent coating of active materials.
Separator Placement Equipment: These devices are responsible for accurately positioning the separator between the positive and negative electrode layers to prevent short circuits.
Winding and Stacking Machines: Prismatic batteries can be assembled using either winding (rolling up the layers like a jelly roll) or stacking (layering) techniques, and dedicated machines are used for these processes.
Tab Welding Machines: Tabs or current collectors are welded onto the electrode foils to establish electrical connections. This is typically achieved through methods such as heat welding or ultrasonic welding.
Formation and Aging Systems: In the formation process, batteries undergo charging and discharging cycles to stabilize their performance. Aging tests simulate the battery's long-term usage and assess its durability.
Cell Enclosure and Casing Machines: These machines are responsible for placing the assembled cells into prismatic-shaped casings, providing physical protection and structural integrity.
Electrolyte Filling Equipment: This equipment injects the conductive electrolyte solution into the battery casing, ensuring proper ion conduction within the battery.
Sealing Machines: Battery casings are sealed to maintain airtightness and prevent leaks. Techniques include laser welding, ultrasonic welding, or adhesive bonding.
Testing and Quality Control Systems: Comprehensive testing equipment is employed for assessing various battery parameters, including capacity, voltage characteristics, cycle life, and safety features. Automated testing ensures accuracy and efficiency.
Module or Pack Assembly Machinery: Depending on the application, prismatic cells are grouped into modules or packs. Assembly equipment connects cells in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity configurations.
Thermal Management Integration: Particularly in electric vehicles, thermal management systems may be integrated into the battery pack to control temperature and prevent overheating, improving safety and performance.
These detailed descriptions encompass the machinery and equipment essential for the precise and efficient production of prismatic lithium-ion batteries. These batteries find use in a wide range of applications and require strict quality control measures to ensure their reliability and safety.


 Subscribe to us
Subscribe to us ONLINE
ONLINE Louis@lithmachine.com
Louis@lithmachine.com +0086 15959378975
+0086 15959378975