Pouch Cell Manufacturing Equipment: Definition, Process, Types, and Key Considerations
Pouch cells are a type of lithium-ion battery encased in a flexible, aluminum-laminated polymer pouch. They are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and energy storage systems due to their lightweight design, high energy density, and customizable form factors. The manufacturing of pouch cells involves precise processes and specialized equipment to ensure consistent quality, safety, and performance.
In this article, we will explore the definition, process, types, applications, advantages, and key considerations of pouch cell manufacturing equipment.
---
●What Is Pouch Cell Manufacturing Equipment?
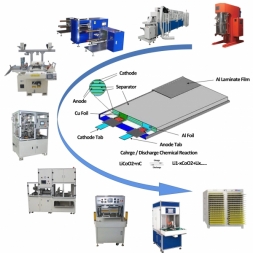
Pouch cell manufacturing equipment refers to the machinery and tools used in the production of lithium-ion pouch cells. These systems are designed to handle various stages of the manufacturing process, including electrode coating, cutting, stacking/laminating, electrolyte filling, sealing, and testing. The equipment ensures that each step is performed with high precision, repeatability, and efficiency.
---
Battery Making Machine
●Pouch Cell Manufacturing Process
The pouch cell manufacturing process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Electrode Coating
- Description: Active materials (e.g., lithium cobalt oxide for cathodes, graphite for anodes) are mixed with binders and solvents to create slurries. These slurries are then coated onto metal foils (aluminum for cathodes, copper for anodes).
- Equipment: Slurry mixers, tape casting coaters, drying ovens.
2. Calendering
- Description: The coated electrodes are passed through rollers to compact the material, improving density and electrical conductivity.
- Equipment: Calendering machines.
3. Cutting
- Description: Electrodes are cut into specific dimensions based on the desired cell size and capacity.
- Equipment: Laser cutting machines, die-cutters.
4. Stacking or Winding
- Description: The cathode, anode, and separator layers are stacked or wound together to form the cell's core structure.
- Equipment: Automated stacking machines, winding machines.
5. Encapsulation
- Description: The stacked or wound core is placed inside an aluminum laminate pouch.
- Equipment: Pouch forming machines.
6. Sealing
- Description: The pouch is sealed around the edges, leaving an opening for electrolyte injection.
- Equipment: Heat sealers, ultrasonic sealers.
7. Electrolyte Filling
- Description: A liquid electrolyte is injected into the pouch to enable ion movement between the electrodes.
- Equipment: Electrolyte filling systems.
8. Final Sealing
- Description: The opening is sealed after electrolyte injection to prevent leakage.
- Equipment: Vacuum sealing machines.
9. Formation and Testing
- Description: Cells undergo formation cycles to activate the electrochemical system and are tested for performance and safety.
- Equipment: Formation chambers, battery testers.
---
●Types of Pouch Cell Manufacturing Equipment
1. Coating and Drying Systems
- Used for applying and drying electrode slurries onto metal foils.
- Examples: Tape casting coaters, slot die coaters, drying ovens.
2. Cutting and Slitting Machines
- Used for precision cutting and slitting of electrodes to specified dimensions.
- Examples: Laser cutters, rotary die-cutters.
3. Stacking and Winding Machines
- Used for assembling the cathode, anode, and separator layers.
- Examples: Automated stacking systems, winding machines.
4. Pouch Forming and Sealing Equipment
- Used for creating and sealing the aluminum laminate pouches.
- Examples: Pouch forming machines, heat sealers, ultrasonic sealers.
5. Electrolyte Filling Systems
- Used for injecting electrolytes into the pouch cells under controlled conditions.
- Examples: Precision filling systems, vacuum filling systems.
6. Formation and Testing Equipment
- Used for activating and evaluating the cells.
- Examples: Formation chambers, cycling testers, EIS analyzers.
---
●Applications of Pouch Cell Manufacturing Equipment
1. Consumer Electronics:
- Smartphones, tablets, laptops, wearable devices.
2. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Powertrains for hybrid and fully electric vehicles.
3. Energy Storage Systems (ESS):
- Grid-scale energy storage, backup power systems.
4. Medical Devices:
- Portable medical equipment, implantable devices.
5. Industrial Applications:
- Robotics, drones, unmanned vehicles.
---
●Advantages of Pouch Cell Manufacturing Equipment
1. High Precision:
- Ensures uniformity in electrode thickness, alignment, and sealing.
2. Automation:
- Reduces manual intervention, increasing throughput and consistency.
3. Customizability:
- Allows for the production of cells with varying sizes and capacities.
4. Safety Features:
- Includes safeguards against overpressure, leaks, and contamination.
5. Scalability:
- Suitable for both small-scale prototyping and large-scale production.
---
●Challenges in Pouch Cell Manufacturing
1. Swelling Issues:
- Pouch cells may swell over time due to gas generation, affecting performance and safety.
2. Sealing Integrity:
- Ensuring airtight seals is critical to prevent electrolyte leakage and moisture ingress.
3. Uniformity:
- Variations in electrode coating, stacking, or sealing can impact cell performance.
4. Cost:
- High initial investment in advanced equipment may deter smaller manufacturers.
5. Complexity:
- Requires skilled operators and regular maintenance to maintain optimal performance.
---
●Key Considerations When Selecting Pouch Cell Manufacturing Equipment
1. Capacity Requirements:
- Choose equipment based on your production volume and scale.
2. Material Compatibility:
- Ensure the equipment can handle the specific materials used in your cells.
3. Automation Level:
- Decide whether you need manual, semi-automated, or fully automated systems.
4. Precision and Accuracy:
- Verify that the equipment meets the required tolerances for coating, cutting, and sealing.
5. Safety Features:
- Look for equipment with built-in safety mechanisms to protect operators and prevent defects.
6. Budget:
- Balance cost with performance and durability when selecting equipment.
7. Support and Service:
- Ensure the manufacturer offers reliable technical support and after-sales service.
---
●Future Trends in Pouch Cell Manufacturing Technology
1. Digitalization and Automation:
- Integration of IoT sensors and AI-driven controls for real-time monitoring and optimization.
2. Advanced Materials:
- Development of new electrode materials and electrolytes for higher energy density and faster charging.
3. Sustainability:
- Focus on eco-friendly designs and recycling processes to reduce environmental impact.
4. Hybrid Systems:
- Combining multiple technologies (e.g., pouch cells with solid-state batteries) for enhanced performance.
5. Energy Efficiency:
- Improving the energy efficiency of manufacturing processes to lower costs and carbon footprint.
---
●Conclusion
Pouch cell manufacturing equipment plays a vital role in producing high-quality, reliable lithium-ion batteries for a wide range of applications. By understanding the different types of equipment, their functions, and key considerations, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and meet the growing demand for advanced energy storage solutions.
What advancements in pouch cell manufacturing technology interest you most? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovations are shaping the future of energy storage and sustainability.


 ONLINE
ONLINE Louis@lithmachine.com
Louis@lithmachine.com +0086 15959378975
+0086 15959378975